Computational Audio
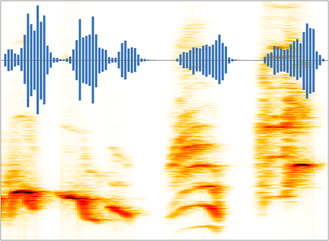
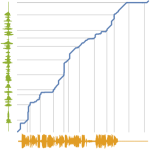
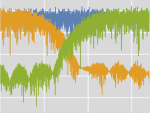
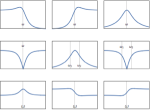
Mathematica Version 11 introduces fully integrated support for audio processing. An audio signal can be stored in-memory for fast computations or linked to a local or remote file. File-based audio representation allows for handling of very large audio files or very large collections of audio files. New capabilities covering audio synthesis, processing, and analysis combined with comprehensive support for signal processing, statistical analysis, and machine learning enable easy prototyping of applications in various fields, including music, speech, communication, and broadcasting.
Key Features
|
|